
Cloud Backup Use Cases and ApproachesĬloud backup has quickly become one of the go-to solutions for organizations seeking offsite storage solutions, with multiple companies opting for its convenience and cost efficiency. A cloud can either be public (like Amazon Web Services ) or private: A public cloud, such as AWS, sells its services across all forms of media, while private cloud offerings typically serve a select group of business users only.

A cloud differs from traditional web hosts in that services offered are on-demand, elastically (clients can take as much or little service as they require), managed centrally, and fully controlled by its provider. What Is The Cloud?Ĭloud computing refers to the delivery of resources and services via the Internet. Their labor savings benefits more than justify any potential additional expenses, such as data transmission fees associated with cloud backup solutions.Ĭloud subscriptions typically cover monthly or yearly billing cycles, and online backup services used primarily by home office users and consumers have since expanded into being used by SMBs for storage of some or all data, offering larger businesses another possible storage option for some or all data needs.

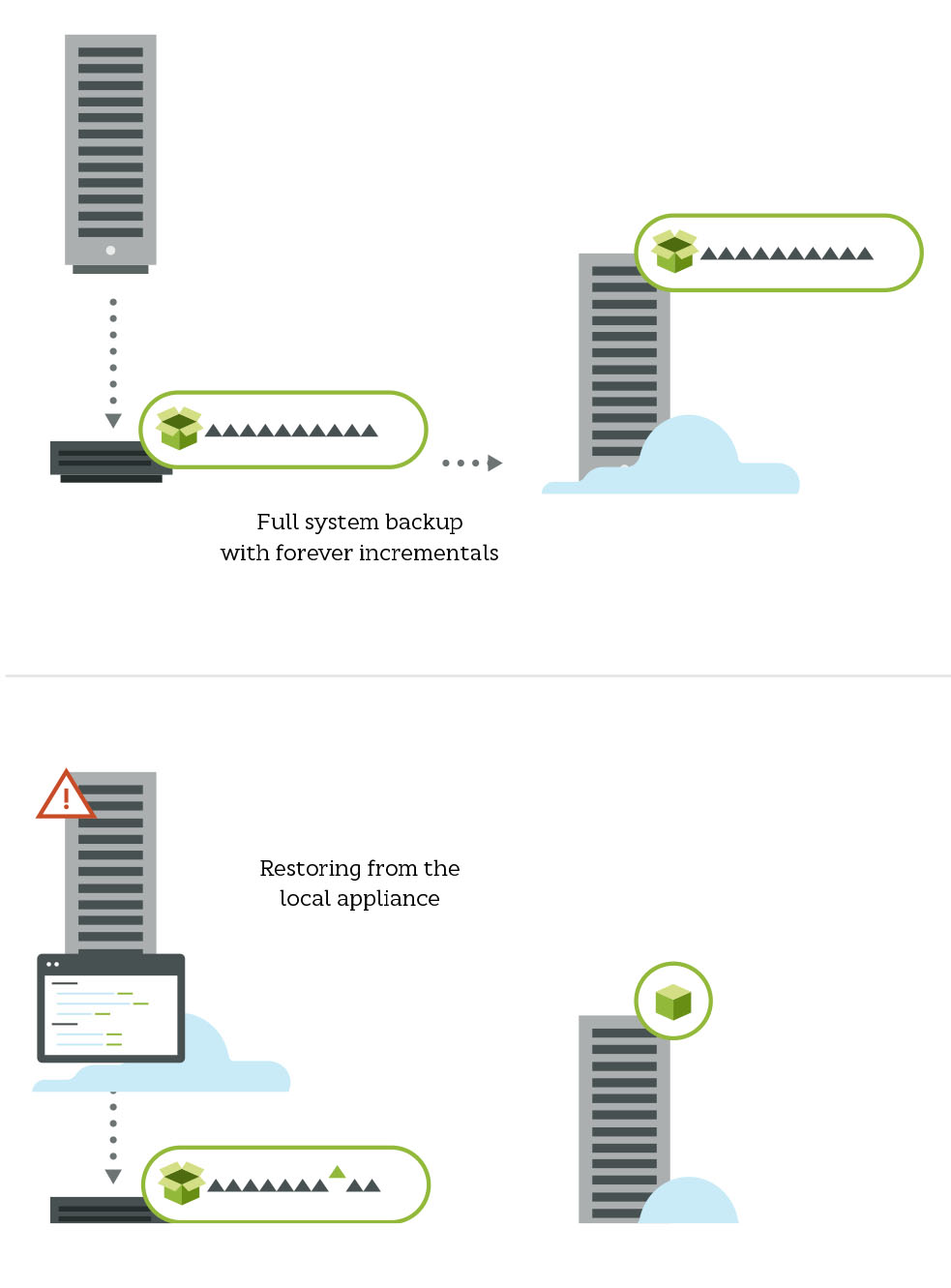
Cloud or SaaS providers typically host these servers and charge monthly for storage or bandwidth.Ĭloud data backup can support an organization's strategies for data protection, regulatory compliance, and business continuity without adding undue strain or costs to IT. Cloud backup strategies (also referred to as online or remote backup) involve sending offsite copies of physical or virtual files or databases in case of disaster, equipment failure, or human error.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
